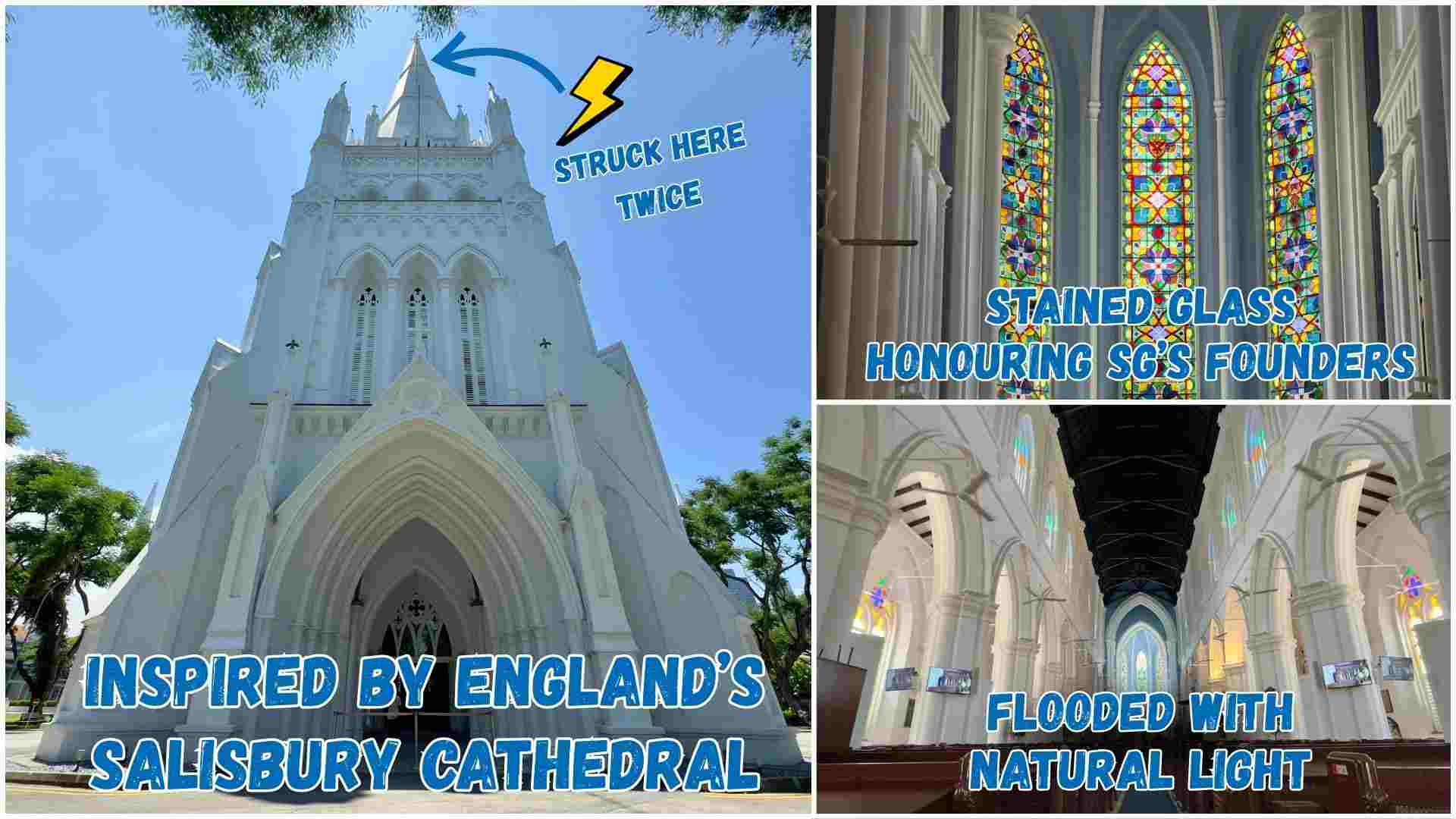
Did You Know There Are Two Ways Of Giving Blood In Singapore?
Singapore Red Cross' #SaveLivesMovement2024 is calling for blood donors to step up and help maintain Singapore's blood supply. With today (14 June) being World Blood Donor Day, there's no time like the present to do your part and begin saving lives. After all, donating blood is a quick and easy way to make a difference, and one unit of donated blood can save three lives.
But did you know there are two types of blood donations you can volunteer for?
1. Whole Blood Donation
When people talk about blood donation, they're usually referring to the more common "whole blood donation". Whole blood refers to blood in its complete form, without being separated into its various components.
When you donate whole blood, it is later separated into its components (red blood cells, plasma, and platelets) for transfusion. Whole blood is seldom used directly for transfusions except in cases of rapid massive blood loss, such as during surgery or for accident victims.
What's the process?
Between 350 ml and 450 ml of blood is drawn. That's only 8% to 12% of the total volume of blood in your body.
How long does it take?
About 5 to 10 minutes.
How often can I donate?
Every 12 weeks.
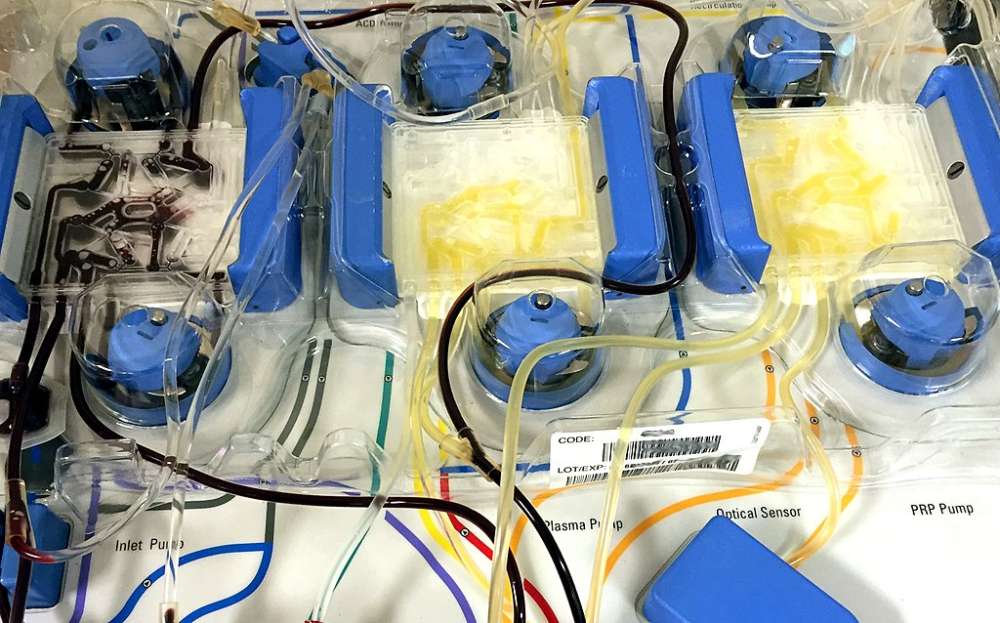 An apheresis machine separates blood into its various components such as platelets, plasma and red blood cells. | IMAGE: NIAID, CC BY 2.0, via Wikimedia Commons
An apheresis machine separates blood into its various components such as platelets, plasma and red blood cells. | IMAGE: NIAID, CC BY 2.0, via Wikimedia Commons
2. Apheresis Donation
Apheresis donation is the lesser-known counterpart to whole blood donation.
Sometimes, patients need only a specific part of a donor's blood. To help these people, donations of individual blood components such as platelets, plasma or red blood cells are required. Such donations are known as apheresis donations.
To undergo apheresis donation, you'll need to:
- Weigh more than 50 kg.
- Be at least 18 years old.
- Be less than 60 years old (if you are an new apheresis donor).
- Have donated blood (whole blood, in other words) at least once.
- Have arm veins of a suitable size.
Common uses:
Red blood cells are used to treat anemia or replace red blood cells that were lost in accidents, during surgery or during childbirth.
Platelets are used to treat dengue, leukemia and cancer patients.
Plasma is used to replace clotting factors which may be depleted in bleeding or infection.
Advantages of apheresis donation:
- Repeat apheresis donors who are below 66 years old can donate plasma and platelet every month, instead of every 3 months for whole blood donations.
- With regular apheresis donations, you can help ensure a stable supply of blood products for patients when they need it.
- Apheresis allows a much larger number of platelets to be collected from a single donor.
- It minimises a patient's exposure to multiple donors' blood.
What's the process?
Apheresis is an automated process. First, machines called blood cell separators draw blood from you. Then, the plasma, platelets or red blood cells (whichever one you're donating) in the blood are extracted. Finally, the remaining components are returned to you.
During the procedure, you might feel tingling around the mouth area or feel a little cold due to the addition of an anti-coagulant called citrate acid to prevent the blood from clotting. This small amount of citrate is broken down very quickly upon infusion.
How long does it take?
60 to 90 minutes for platelet donation, and 45 minutes for plasma and double red cell donation.
How often can I donate?
Platelets and plasma: Every four weeks.
Double red cells: Every 16 weeks.
For the latest updates on Wonderwall.sg, be sure to follow us on TikTok, Telegram, Instagram, and Facebook. If you have a story idea for us, email us at [email protected].